Content
Table of Contents
- Background Introduction
- Specific Implementation
- Specific Steps
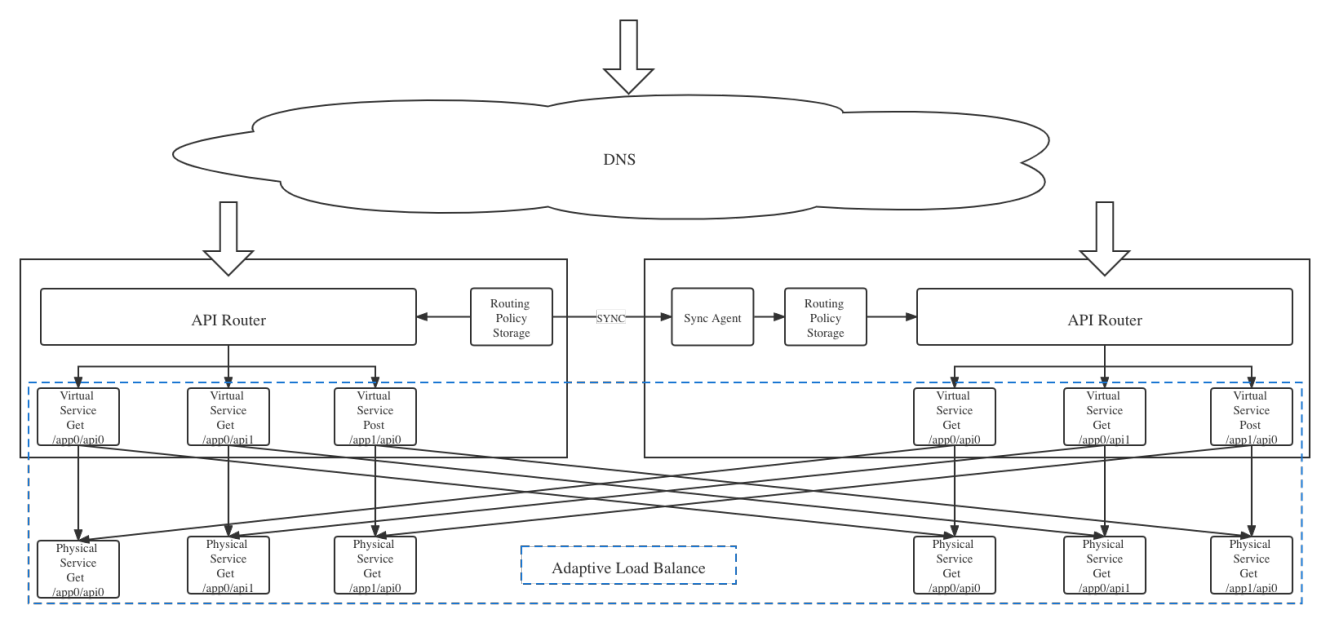
- 1. The request is sent to the virtual server through the API route
- 2. The virtual service sends a request to the backend physical server according to the adaptive dynamic load balancing mode
- 3. The backend server processes the request and returns, and the shared memory updates the number of transactions and the network delay value
- Specific Steps
- Difficulty
- Key technical points
- Patent application
Background Introduction
A method and device for multi-data center API traffic scheduling mainly realizes the synchronization of routing rules between multiple data centers or computer rooms, and supports two schemes: preset configuration forwarding and adaptive forwarding. It also specifically explains how to implement a request forwarding method that does not rely on preset tags. It also comprehensively considers the real-time request processing capability and load of the backend server, and proposes an adaptive load balancing mode, which better overcomes the defects and problems existing in the above background technology schemes.
Specific Implementation
Specific Steps
1. The request is sent to the virtual server through the API route
DNS sends the request to the API route of the corresponding cluster, the API route reads the routing policy from the corresponding cluster configuration center, and the API route sends the request to the virtual server according to the corresponding routing policy.
2. The virtual service sends a request to the backend physical server according to the adaptive dynamic load balancing mode
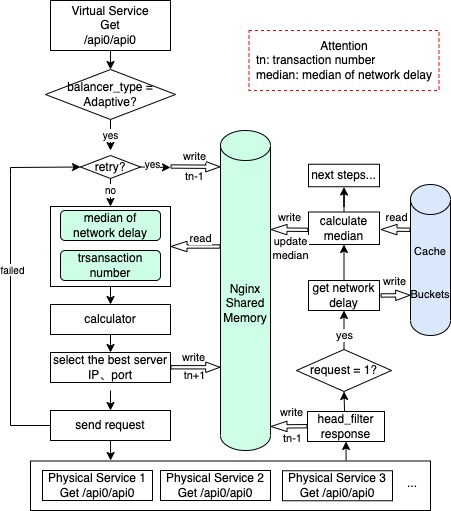
The request enters the load balancing module through the Upstream module. If the load balancing mode is “Adaptive”, it enters the adaptive load balancing mode;
Traverse all backend servers and read the number of transactions and network delay values stored in the nginx shared memory with the server IP address, port number, and process id as indexes;
Calculate the response time of the server, multiply the number of transactions by the square of the network delay, where the exponential power of the network delay is an adjustable parameter (response_time = transaction_number * pow(network_delay, 2));
If the weight value is set in advance, the updated response time is the response time multiplied by 10000 and divided by the weight (response_time = response_time * 10000 / weight);
Determine whether the request is a re-entry. If so, reduce the number of stored transactions by one. Store the backend server IP address, port number and other related information required by Nginx, and add one to the number of transactions corresponding to the server.
3. The backend server processes the request and returns, and the shared memory updates the number of transactions and the network delay value
The backend server returns the request to the header_filter module, indicating that a request is completed. If the load balancing mode is “Adaptive”, the number of transactions corresponding to the server processing the request is reduced by one;
Use Nginx built-in variables to obtain the network delay of the first connection with the server and the number of requests under the current connection;
If the number of requests under the current connection is 1, it means that the obtained network delay value is the first connection delay, and the count value of the bucket corresponding to the connection delay is increased by one, and the upperBound value in the bucket is updated;
Use the bucket data to calculate the median of all network delays, and use the median to update the original median value of the server.
Difficulty
Problem 1
Problem description: When the amount of data is too large to be sorted and the data continues to increase, how to calculate the median more accurately without consuming too much memory and time
Solution: Study the function histogram_quantile() in prometheus for solving quantiles. This algorithm sets up many buckets for real-time calculation of the median of the statistic. Each bucket stores the total number of counts falling into the bucket. The count is used to estimate which bucket the median is approximately in, and the linear interpolation method is used to calculate the approximate median value. This method takes up little memory space. Each bucket only needs to store two values: count and the maximum value counted in the bucket. In this case, 14 buckets are set according to the distribution of network delay. At the same time, this method only sorts these dozen buckets, and does not need to sort all sample data. The total time cost is very small. The calculated median error is related to the bucket setting, so the median error is also within the controllable and acceptable range. This algorithm solves the problem well.
Using the median of network delay instead of the instantaneous value of network delay as the influencing factor improves the stability of the entire load balancing system, prevents the jitter of the network, increases the instantaneous network delay, causes the request to be sent to the back-end server with lower request processing efficiency, and prevents the server from being unable to receive requests and update the network delay in time after the network returns to normal for a period of time. At the same time, stable network delay data can also more objectively reflect the distance between the request end and the receiving end server. This operation performs a first-level smoothing process on the influencing factor of network delay, which guarantees the stability of the system to a certain extent.
In the process of calculating the median, the traditional method that requires a lot of memory to retain the original data and a lot of time to sort the original data is not used, but a median estimation method based on statistics is adopted. This method only needs to divide dozens of buckets according to the distribution range of network delay, and each bucket only stores the total number and maximum value falling into the bucket, which greatly saves memory space. In the traditional approach, the cumulative histogram method is required, that is, the bucket.count before the current bucket is accumulated as the new bucket.count, so that when some data needs to be discarded, the data can still be guaranteed to be within a certain accuracy range. However, in this patent, the maximum value of bucket.count before the current bucket is used as the new bucket.count, so that when taking the 50% quantile (ie, the median), it can be ensured that the median calculation result is not too divergent, the difference between each calculation result is reduced, and the lost precision can be ignored because of the subsequent proportional evaluation. Therefore, without adding additional time and space overhead, the network delay factor is smoothed at the second level, ensuring that each server in the performance test and actual production environment, especially when processing high concurrent requests, maintains great stability.
Problem 2
Problem description: Occasionally, in the test, the machine with the lowest network latency will have its QPS drop after running for a period of time, and there is no regularity to follow
Solution: Preliminary analysis shows that the conflict between golang scheduling cpu and container scheduling cpu leads to some resource deadlocks, high transaction counts, increased latency, and finally the load balancing abandonment of the machine. Therefore, uber-go/automaxprocs is used in the project to automatically set GOMAXPROCS to match the allocation of cpu in Linux containers.
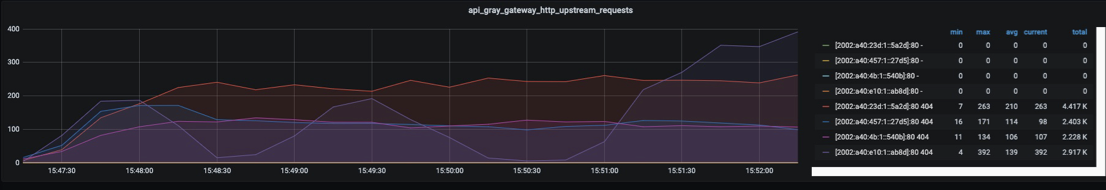
Before solution: As shown in the figure below, unstable cpu scheduling leads to irregular jitters in QPS.
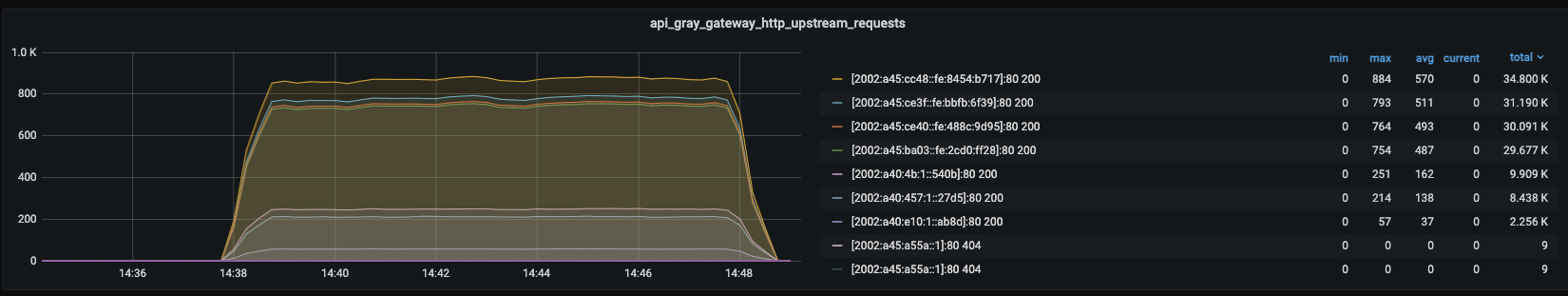
After the solution: In the high concurrency (500connection) scenario, the load balancing works normally and the QPS is relatively stable.
Key technical points
- resty.lrucache
Use cache to store buckets for calculating medians
- ngx.shared.dict
Use shared shared memory to store transactionNumber and networkDelay. The key in the key-value pair distinguishes different hosts, different ports, and different process ids ngx.worker.id() to avoid dirty read problems caused by concurrency.
- Increase or decrease transactionNumber
-
It is necessary to set a label to determine whether it is a re-entry;
-
After executing load balancing, transactionNumber needs to be increased by one;
-
Successfully received return, that is, transactionNumber needs to be reduced by one after headfilter/bodyfilter;
Patent application
patent address: https://patents.google.com/patent/CN114553881B/en?oq=CN114553881B
